A string in Golang is a sequence of characters with a definite length and is used to store the text.
- Declare String Variable in Golang
- Initialize String in Golang
- How Strings are stored in Golang
- Access any particular character of a String in Golang
- Find the Length of String in Golang
- Concatenation of strings in Golang
- References
Declare String Variable in Golang
You can use the string keyword to declare a string variable in Golang. The default value given to a string variable is an empty string (“”)
var x stringInitialize String in Golang
You can initialize a string in Golang using different ways.
- Double quotes notation
- Double quote string initialization cannot contain a new line in the string.
- Special escape sequences are allowed like \n for new-line and \t for tab character
var x string = "Code With Raj Ranjan"- Back Tick notation
var x string = `Code With Raj Ranjan`How Strings are stored in Golang
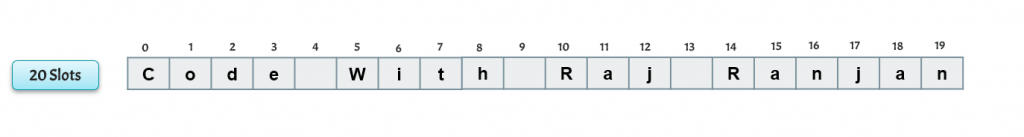
A string is a sequence of characters. You can think as if each character has been assigned their slot. The slot number starts from zero and ends at one less than the length of string.
- Let’s take the string “Code With Raj Ranjan“
- The length of a string is equal to the count of all the characters including white spaces.
- For the above string, the length will be 20
- lowest index will be 0
- the highest index will be 19
- we need to take a box having 20 slots and then fill each character in the slot.
Access any particular character of a String in Golang
You can use the bracket notation and use the index of that character to access that particular character of the string. You can access the character at the third index using the below code.
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x string = `Code With Raj Ranjan`
characterAtThirdIndex := x[3]
fmt.Println(characterAtThirdIndex)
}➜ hello-world go run main.go
101You can see in the above output that the value returned will be the ASCII value of the character and not the actual character. The character at the third index is e and the ASCII value of e is 101
If you want to print the character value then you need to use the %c with the Printf method
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x string = `Code With Raj Ranjan`
characterAtThirdIndex := x[3]
fmt.Printf("%c", characterAtThirdIndex)
}➜ hello-world go run main.go
e If you provide the index value in negative then it will give you an error
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x string = `Code With Raj Ranjan`
// here we are accessing index as -10
characterAtThirdIndex := x[-10]
fmt.Println(characterAtThirdIndex)
}➜ hello-world go run main.go
# command-line-arguments
./main.go:7:29: invalid argument: index -10 (constant of type int) must not be negative If you access the index value greater than the size of the string then again it will throw an error
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x string = `Code With Raj Ranjan`
characterAtThirdIndex := x[100]
fmt.Println(characterAtThirdIndex)
}➜ hello-world go run main.go
panic: runtime error: index out of range [100] with length 20
goroutine 1 [running]:
main.main()
/home/selftuts/workspace/go/hello-world/main.go:7 +0x17
exit status 2 Find the Length of String in Golang
Golang provides the len function to find the length of a string
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x string = `Code With Raj Ranjan`
// using the len function on the string to find the length of the string
lengthOfString := len(x)
fmt.Println(lengthOfString)
}➜ hello-world go run main.go
20 Note: The length of the string also counts the whitespace characters
Concatenation of strings in Golang
Add of two strings to produce a unified one string is called concatenation. In Golang you can concatenate two strings using the plus (+) operator
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var firstString string = `Code With `
var secondString string = `Raj Ranjan`
thirdString := firstString + secondString
fmt.Println(thirdString)
}➜ hello-world go run main.go
Code With Raj Ranjan